A recent study in mice investigated the health effects of elevated levels of muscle NAD+ after daily IV injections of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR).
Key Points:
- Oral NR failed to increase NAD+ levels
- NR injections boosted NAD+ levels in the skeletal muscle and adipose tissue
- Exercise & NR injections were more effective when combined
- Exercise and NR injections protected against weight gain
Animal Study Compares Oral vs. Intravenous Administration of NR
A study on 64 mice fed with a western diet consisted on 2 phases:
The first phase assessed muscle NAD+ levels after 7 days of IV NR (200 mg/kg) compared to oral administration.
The second phase investigated the effect of chronically elevated levels of NAD+ after 4 weeks of daily NR injections (100 mg/kg) on insulin sensitivity, mitochondrial respiration and weight gain compared to controls, voluntary exercise and NR plus exercise.
Daily NR Injections Led to a Sustained Increase in NAD+ Stores
NR injections boosted NAD+ levels in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue.
A ~140% increase in muscle NAD+ was observed after 7 days of IV administration of NR. Oral administration failed to increase NAD+ levels compared to the control group (figure A).
NR content in muscle increased 36-fold after IV delivery compared to no increase after oral administration (figure B).
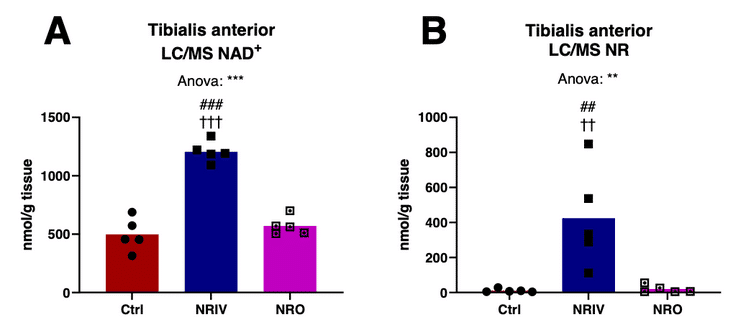
NR supplementation seems to act in multiple peripheral tissues. These elevated levels of NAD+ in the muscle and adipose tissue were sustained over ~18 h after NR injection.
“These findings reinforce the observation that orally supplemented NR is not directly bioavailable to skeletal muscle, but that this can be circumvented by IV delivery, (…) which bypass intestinal degradation and first-pass metabolism in the liver and make NR directly available to peripheral tissues.”
Liposomal delivery could be presented as an alternative to improve the bioavailability of the poorly absorbed NR oral delivery.
Exercise Improves Uptake of NR Supplementation
Quadriceps NAD+ content increased to a greater extent in active vs. sedentary mice after NR injections. Exercise appears to enhance NR uptake or help retain NAD+ in the muscle.
“In sedentary mice, the daily NR injections increased NAD+ levels by ~13%, whereas NR increased NAD+ levels by ~30% in mice with access to running wheels.”
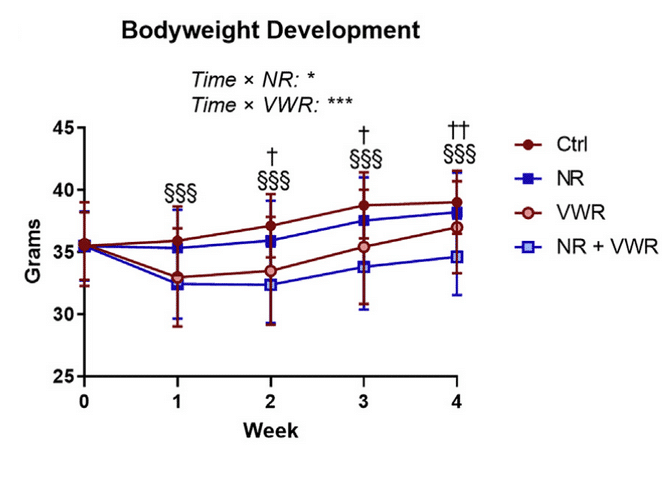
Exercise and NR Protected Against Weight Gain
Voluntary wheel running, NR injections, and especially its combination protected against Western diet-induced weight gain.
This could be due to a reduction in hunger as a result of NR supplementation, which led to a reduction in energy intake.
However, NR supplementation did not affect insulin sensitivity or mitochondrial respiration.
Conclusion
Daily NR injections boosted NAD+ levels sustainedly in peripheral tissues compared to oral supplementation, which failed to increase NAD+ levels.
“In conclusion, we successfully and stably increased the NAD+ pool in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue by the daily intravenous injection of NR.”
